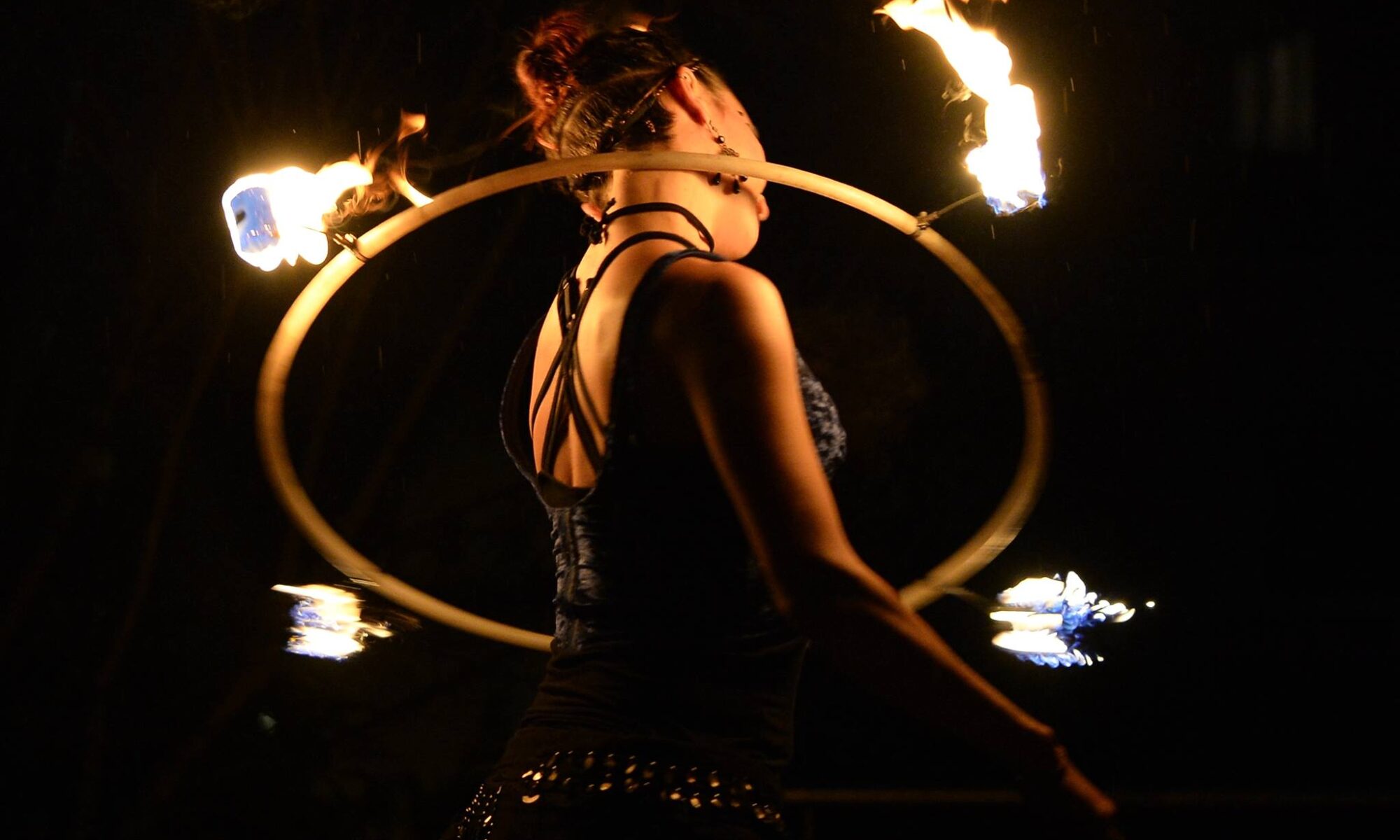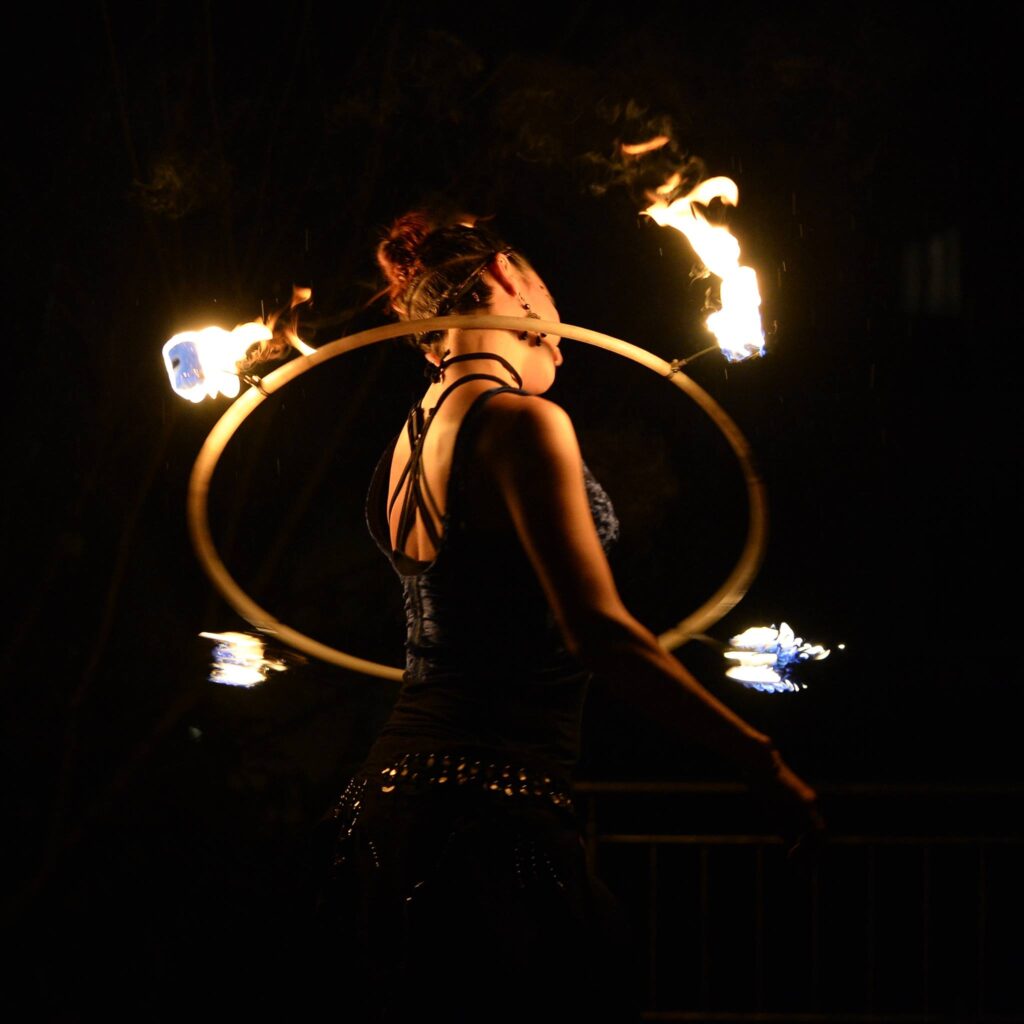From Anxiety to Aliveness
How Creativity Helps Us Heal
Is your mind sometimes spinning stories you didn’t sign up for?
You’re not alone.
Since the pandemic, global anxiety levels have skyrocketed—rising by over 25%, according to the World Health Organization. And in today’s fast-paced, overstimulated world, our brains are more vulnerable than ever to getting caught in what psychologists call a negativity bias—a tendency to dwell on threats, worries, and worst-case scenarios. Add in doomscrolling, algorithm-driven fear loops, and constant performance pressure… the perfect recipe for the “anxiety spiral.”
..so what can we do?
“The opposite of anxiety isn’t calm—it’s creativity.” Dr Martha Beck
....be curious!
The Creative Antidote to Fear
At MetaMoreFire, we believe in the power of the present moment—and in the magic that happens when we stop running and start expressing. Whether it’s through fire dance, scribbling, storytelling, or movement, creativity has a way of flipping the switch in our brain.
And that’s not just poetic—it’s neuroscience.
Dr. Judson Brewer, a leading psychiatrist and neuroscientist, explains in his book Unwinding Anxiety that curiosity is a game-changer for anxious brains. Why? Because curiosity activates different brain regions than fear—specifically, the areas responsible for learning, play, and innovation. When we get curious, the brain literally can’t stay in panic mode.

So when you start painting, dancing, or shaping a new idea—you’re not just “being creative.” You’re giving your brain a new path out of fear.

Whole Brain Living and Flow States
Creativity isn’t a “left brain” vs. “right brain” thing. It’s about connecting both hemispheres. As Dr. Jill Bolte Taylor shares in Whole Brain Living, engaging in artistic expression strengthens the right brain (emotion, context, and presence) and helps balance the left brain (logic, language, planning).
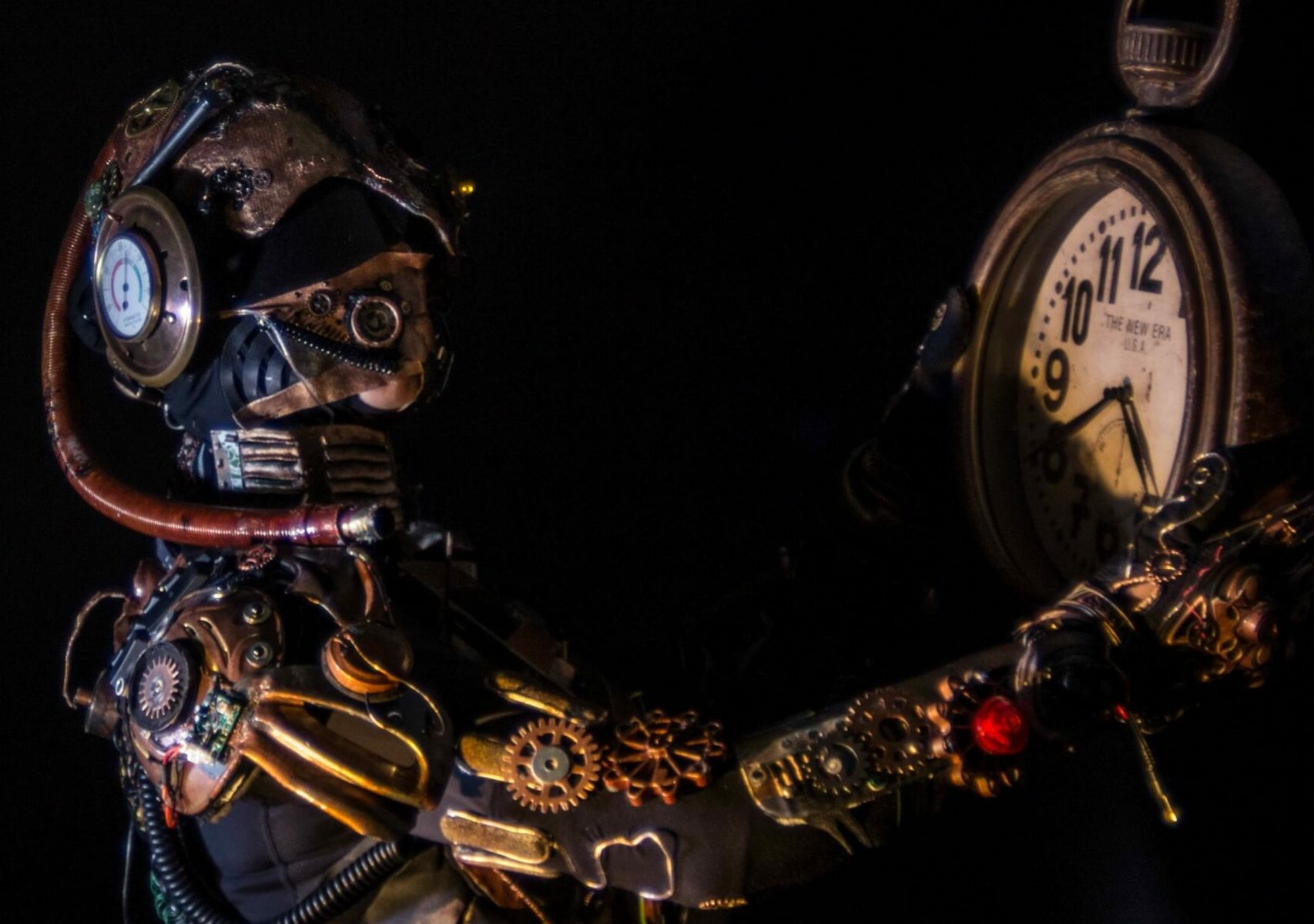
This harmony is what Flow Artists call “the state of flow”—a moment when time slows down, the inner critic quiets, and you become fully immersed in the now.
And at MetaMoreFire, this now is sacred. Its the moment of CHANGE.
Creating Your Sanctuary
We often externalize our anxiety—through overloaded calendars, noisy notifications, even the architecture of our environments. But healing begins with reclaiming space—internal and external—where your nervous system can breathe.
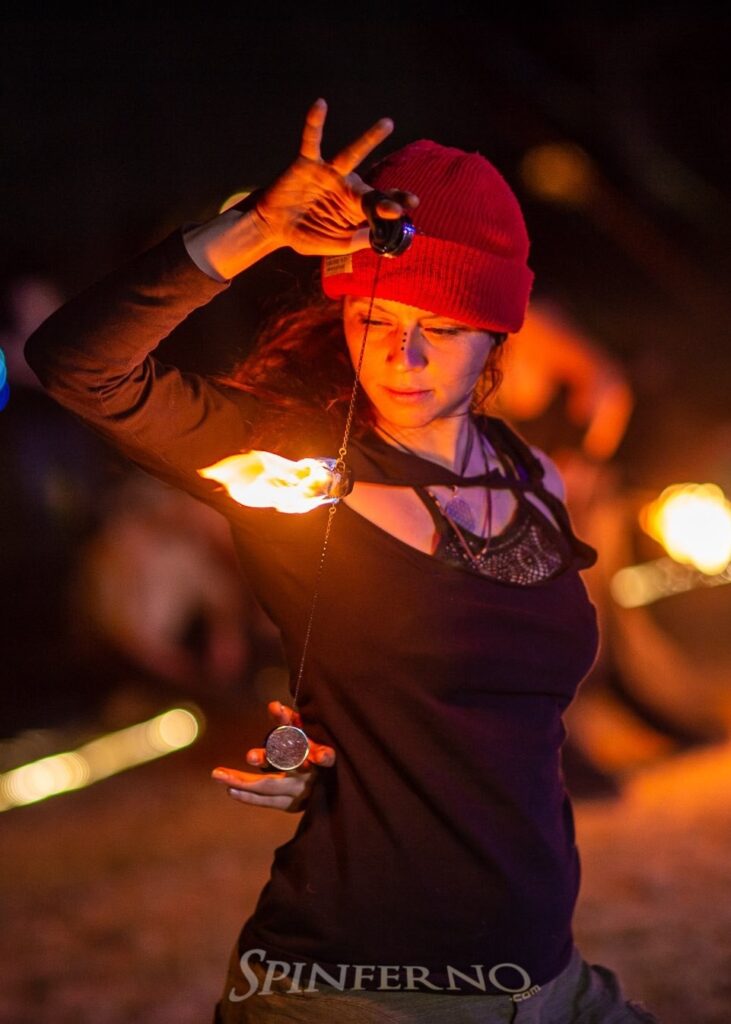

Search for Glimmers
Polyvagal theory therapist Deb Dana calls these safe, soothing experiences “glimmers”. These small moments of beauty, nature, or connection help reset our systems.
Let art be your refuge.
“Fire dancing gave me back my life energy. It grounds me in the present moment, opens gates of creativity, and has become my favorite form of artistic expression.”
Christiane Meyer, Director’s Statement, MetaMoreFire
Art as Presence, Not Perfection
You don’t have to be “good at art” for creativity to work its magic.
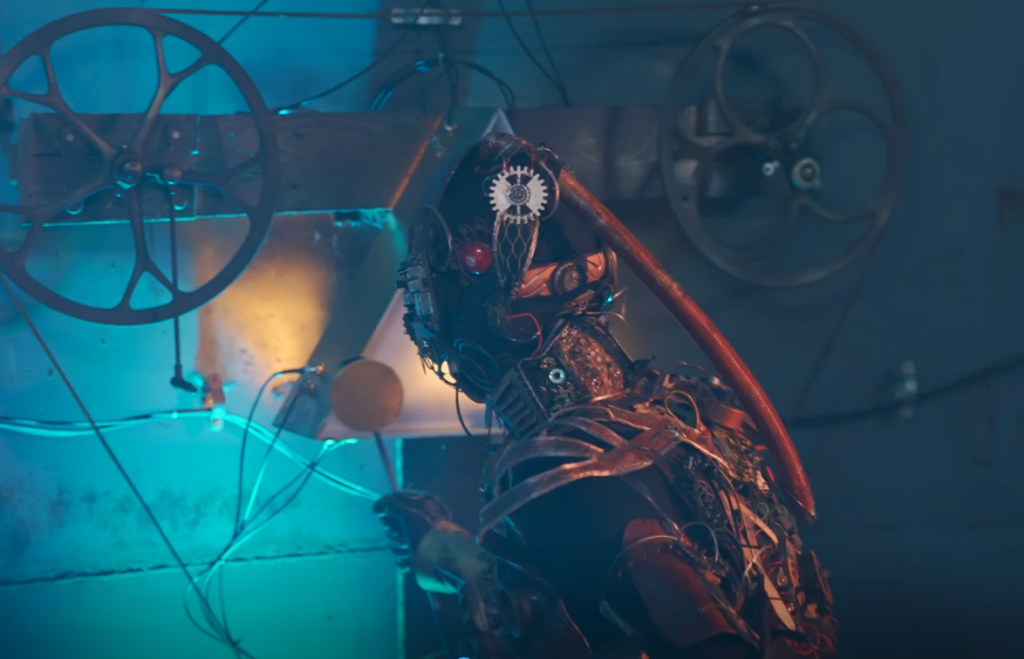
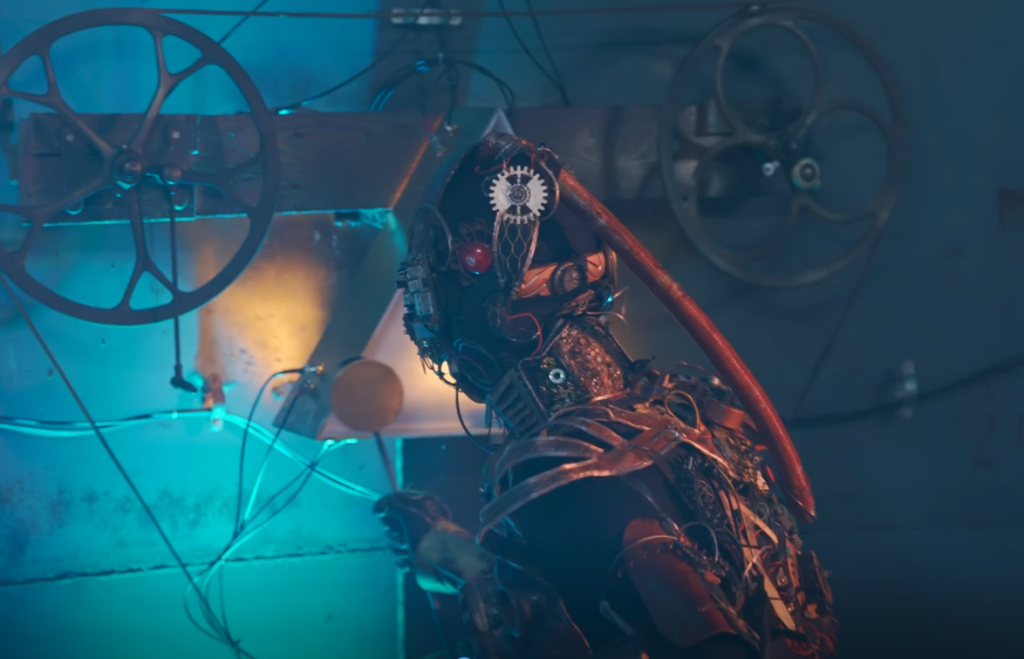
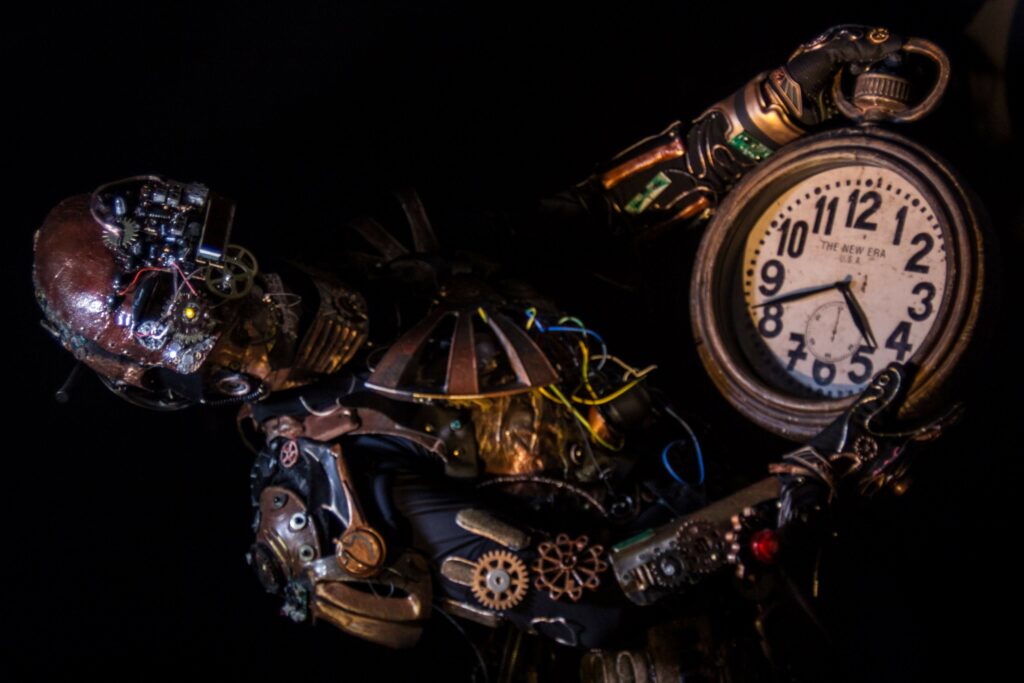
At MetaMoreFire, we don’t perform to impress—we express to transform. Our film began as a deeply personal journey of healing trauma through fire dance.
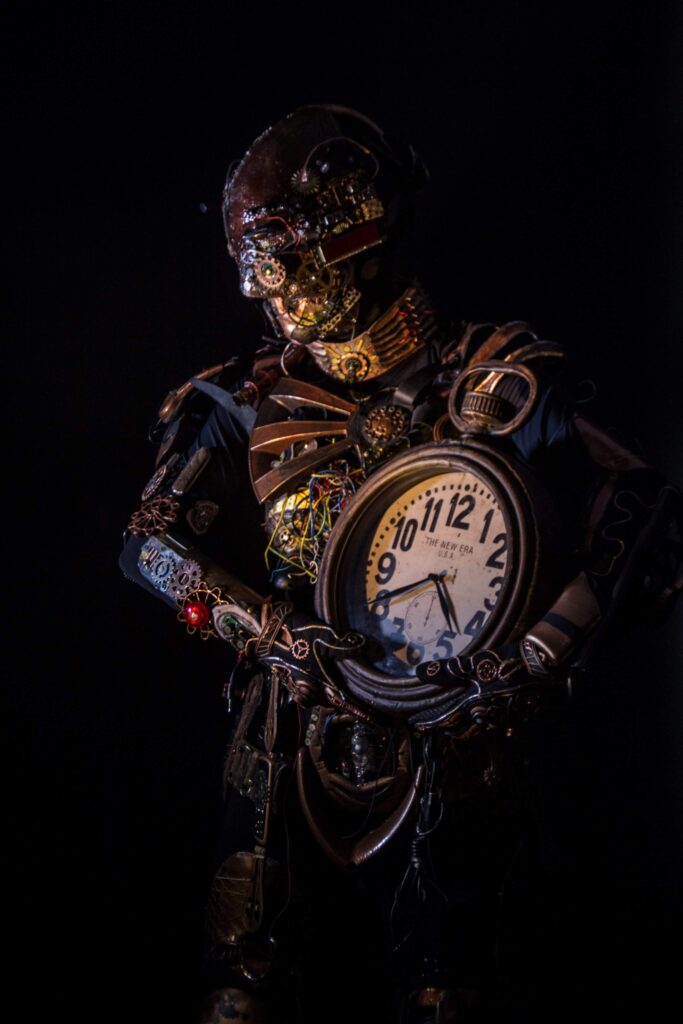
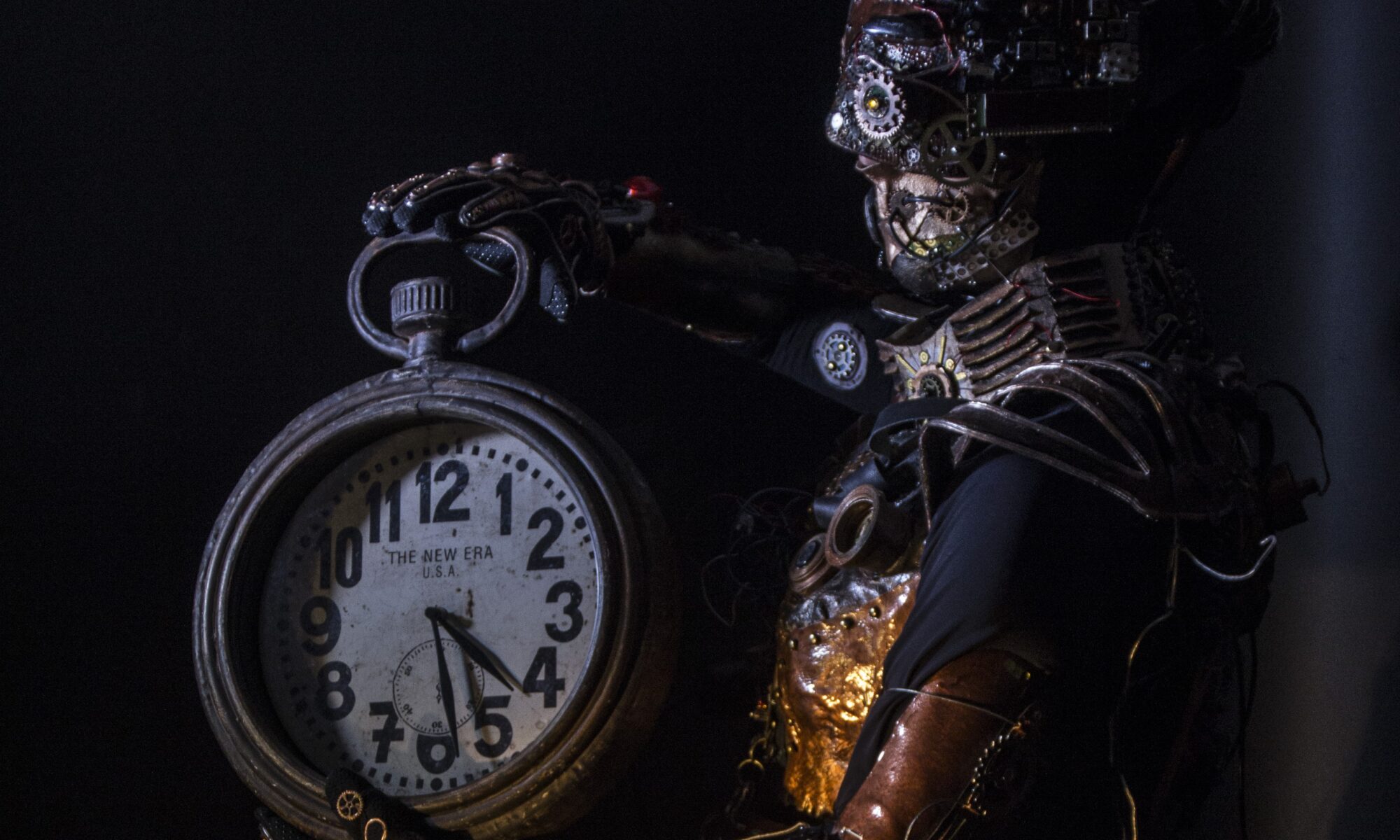
It became a powerful metaphor: from robot to human, from numbness to presence, from fear to freedom.
Practical Tips to Ease Anxiety through Creativity
Here’s how you can begin using creativity as a daily anxiety-relief tool:
Make something with your hands – clay, paint, paper, yarn, whatever. Tactile actions ground the body.
Dance to a single song a day – let your breath and movement reconnect.
Create without judging – scribble, doodle, write, sing badly—just do it.
Set a “tech-free” creative hour – where input becomes output.
Be curious about your fear – talk to it like a scared animal. Ask: “What do you need right now to feel safe?”
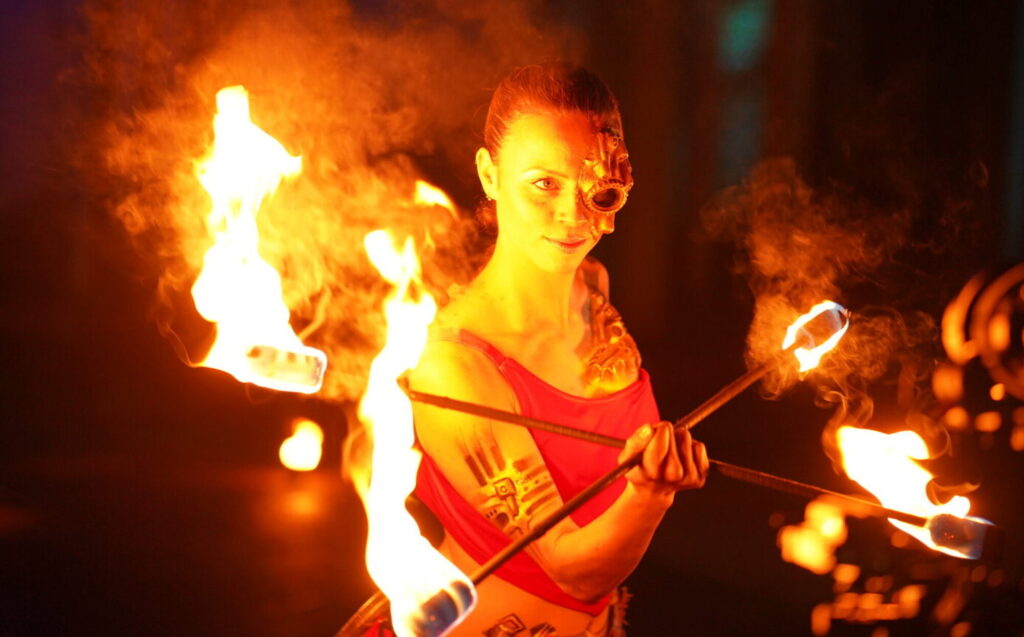

Why This Matters Now
We live in a culture that moves too fast and values doing over being. But as ancient Eastern philosophies and modern neurobiology both show—stillness is powerful. When we stop time through creativity, we rediscover ourselves.
That’s why MetaMoreFire was created: to celebrate the intersection of consciousness, art, and inner freedom.
You’re not broken. You’re becoming.
Dive into our film and story at www.metamorefire.com
Follow our behind-the-scenes on Instagram @MetaMoreFire
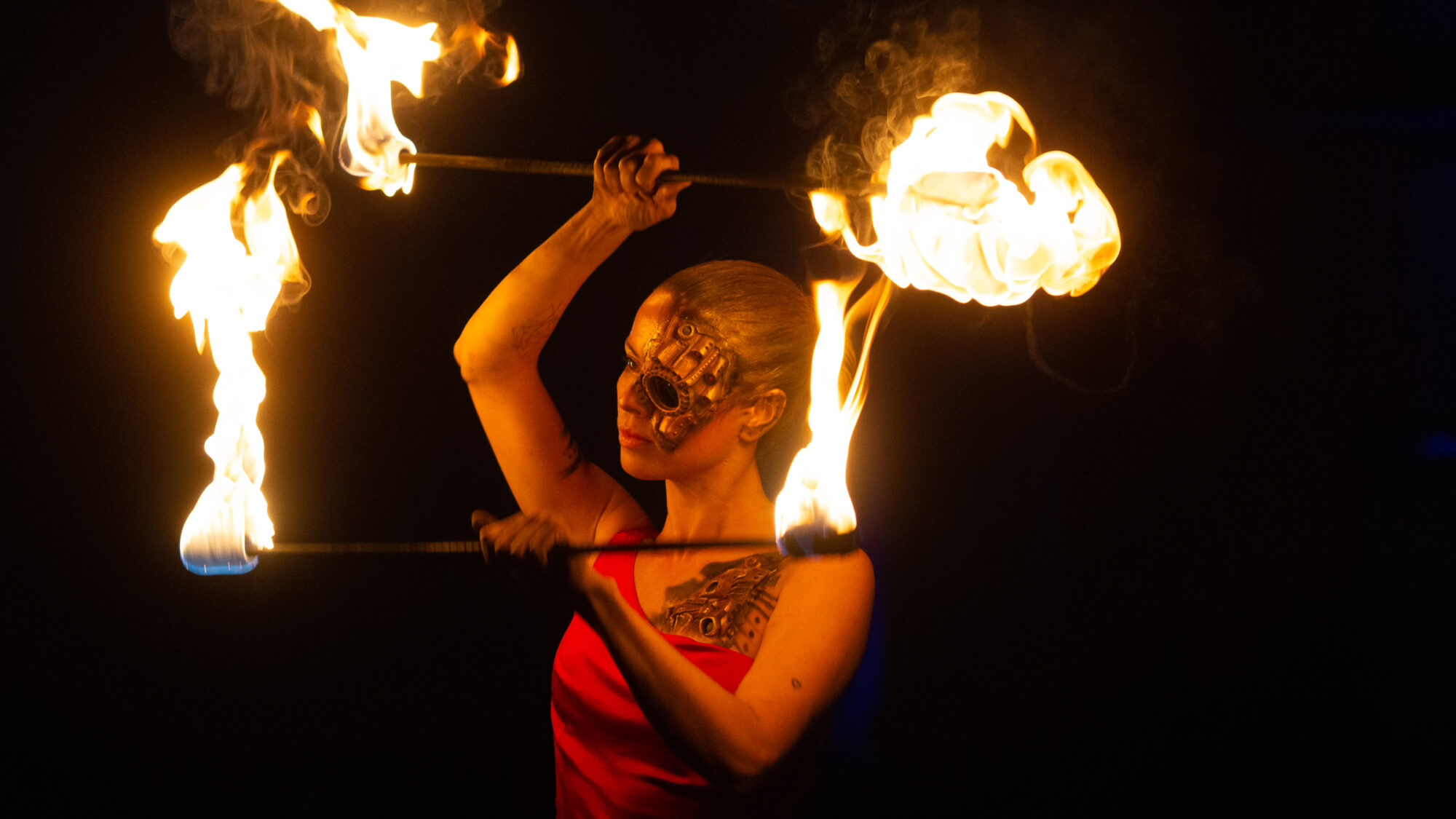

 Metamorefire – Copyright by Miigaa
Metamorefire – Copyright by Miigaa 
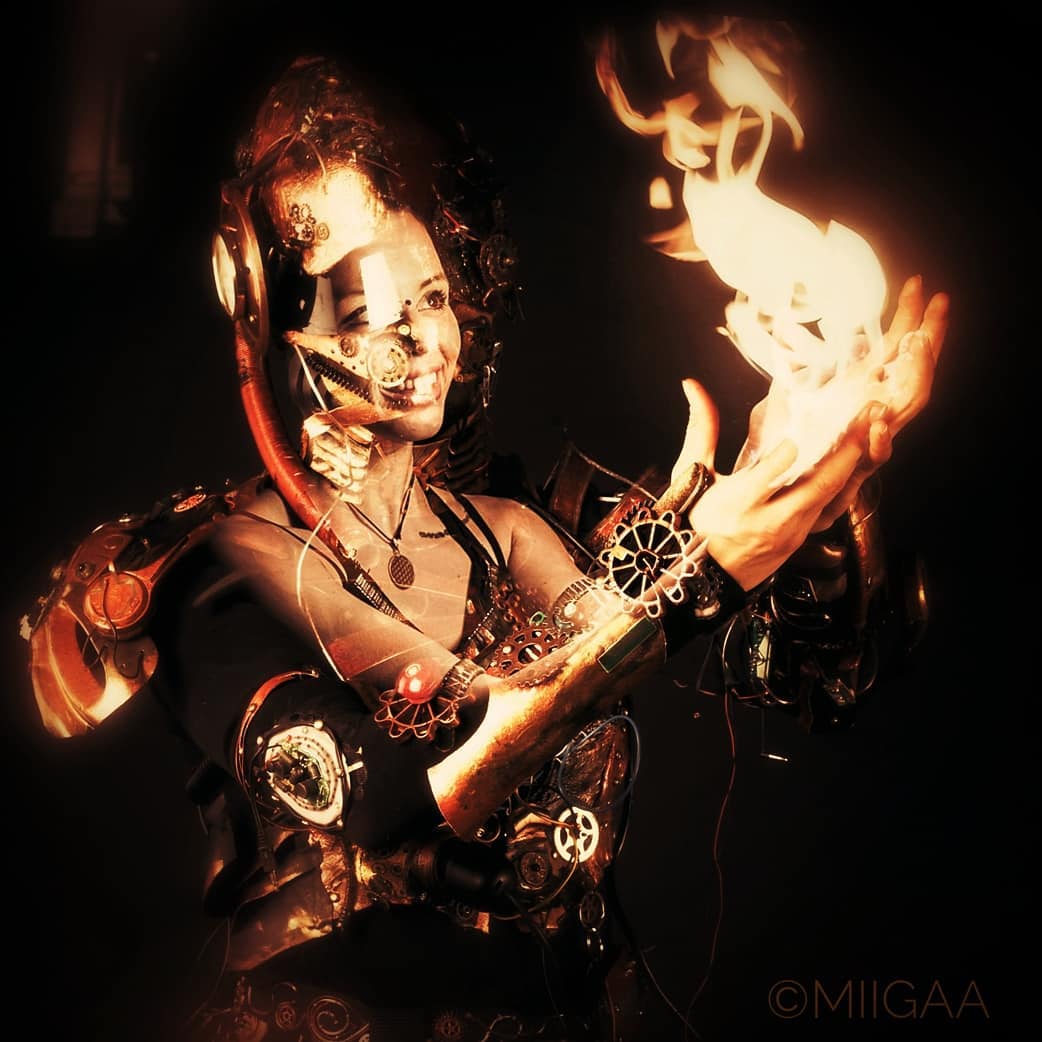
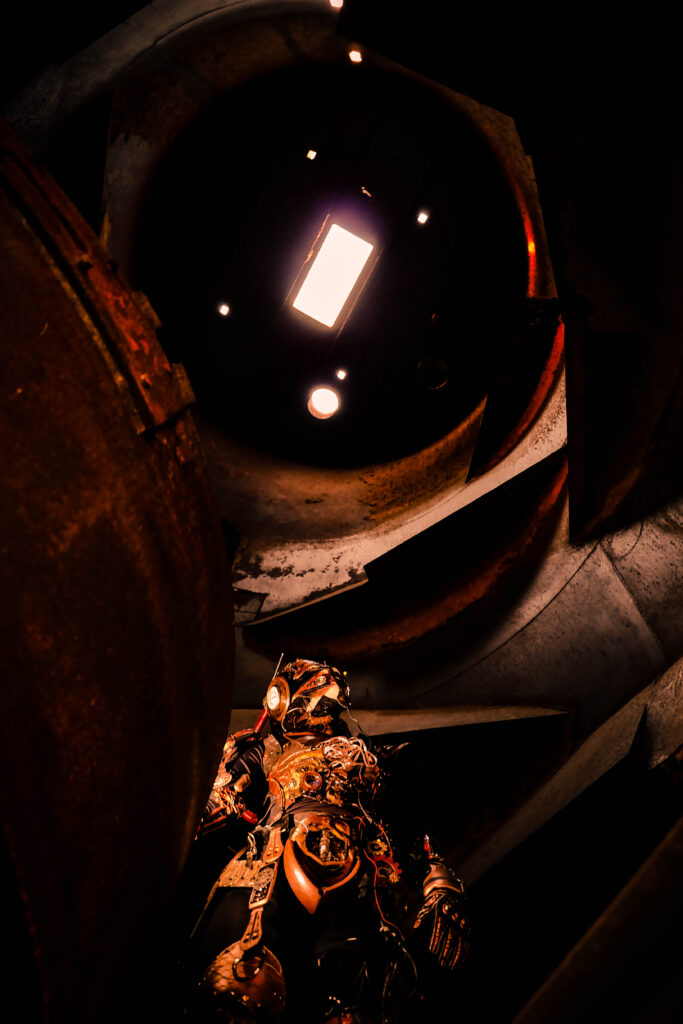




 Movement, dance, and self-expression can help release pent-up stress, just as they do in the film’s narrative.
Movement, dance, and self-expression can help release pent-up stress, just as they do in the film’s narrative. Global Hotlines:
Global Hotlines:
 Text HELLO to 741741 (USA, UK, Canada)
Text HELLO to 741741 (USA, UK, Canada) United States
United States 988 (
988 ( 1-800-950-6264 (
1-800-950-6264 ( United Kingdom
United Kingdom Canada
Canada Australia
Australia Germany
Germany France
France Italy
Italy Spain
Spain India
India South Africa
South Africa If you or someone you know is in immediate danger, please call emergency services (112 / 911 / local equivalent).
If you or someone you know is in immediate danger, please call emergency services (112 / 911 / local equivalent).